By eating a balanced diet before and during pregnancy and while breastfeeding, you give your baby the best chance for a good start in life. So you both get the right amount of energy and nutrients. In addition, it allows you to positively influence the course of pregnancy and childbirth, thereby promoting the healthy development of the child.
WEIGHT CHANGES DURING PREGNANCY
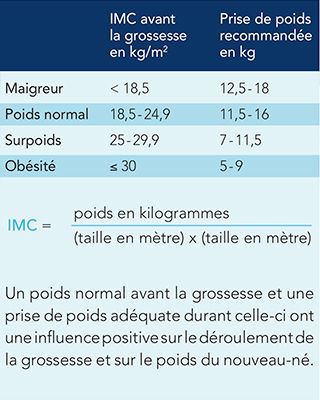
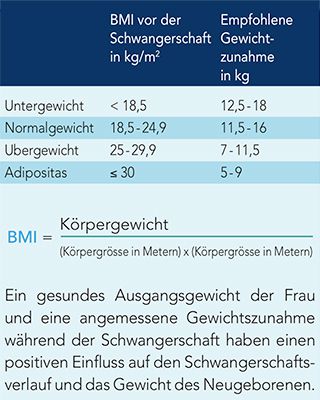
The recommended weight gain during pregnancy depends on your weight before pregnancy. The table below shows the optimal weight gain in each case.
FOOD DURING PREGNANCY AND BREASTFEEDING
Although your body is very stressed during pregnancy, your energy needs only increase slightly, and only from the 4th month. From then on, you need about 250 kcal more per day than before you became pregnant. Only certain vitamins and certain minerals may be missing. If necessary, your gynecologist can prescribe food supplements.
Namely that 5 nutrients are essential during pregnancy. These are folic acid, vitamin D, iron, iodine, and omega-3 fatty acids.
ENERGY AND NUTRITIONAL NEEDS DURING THE BREASTFEEDING PERIOD
During the breastfeeding period, the mother’s body produces 780 ml of milk per day, which leads to a sharp increase in energy requirements. Some of the energy required can be taken from the fat reserve accumulated during pregnancy. Breastfeeding will therefore allow you to shed extra pounds. The rest of the required energy (approx. 500 kcal) can be taken from the food, eg. ex. by eating 2 slices of wholemeal bread with 2 pieces of cheese, or muesli with cereal flakes, fruit, nuts, and milk. If you are only partially breastfeeding, your energy needs will increase little, and if you are not breastfeeding, they will not increase.
FOLIC ACID: AN ESSENTIAL VITAMIN
Folic acid (or vitamin B9) is also an important element during the pre-conception period and during gestation. It is involved in many functions of our body and is linked to the production of genetic material, cell division, as well as the formation of red blood cells and the immune system.
Before and after pregnancy, the body’s need for folic acid increases. Deficiency can be very damaging during pregnancy, including causing malformations of the nervous system of the embryo and the threat of neural tube defects such as spina bifida. Studies have shown that folic acid prophylaxis significantly reduces the risk of premature births or miscarriages.
It is therefore recommended that women planning to become pregnant and those who are already pregnant seek advice from their doctor or gynecologist on this subject.
“Do not drink a drop of alcohol when you are breastfeeding because the alcohol passes directly into your milk and therefore into your baby’s body.”


SHOULD WE EAT MORE?
Your energy need depends on a wide variety of factors, such as the stage of breastfeeding, the amount of milk your baby is consuming, and your activity level. Your energy comes as much from the food you eat as it does from the layers of fat stored during pregnancy. So you will not always need to eat more but to eat “better”.
WHAT ABOUT THE DRINKS?
To meet your increased needs, drink a minimum of 1.5 to 2 liters per day. This is essential because this extra liquid is used to replace the liquid you give through your milk. All drinks contribute equally to fluid intake, although water, skimmed milk, and fruit juices are the best choices to quench your thirst.
Do not drink a drop of alcohol when you are breastfeeding because the alcohol passes directly into your milk and therefore into your baby’s body.
CRITICAL FOODS FOR PREGNANT OR BREASTFEEDING WOMEN
Some fish have high levels of methylmercury, dioxins, and dioxin-like compounds. Vary the different kinds of fish. During pregnancy and while breastfeeding, you should avoid or limit the consumption of the following:
- Marlin (marlin), swordfish, shark, and Baltic Sea salmon and herring should be avoided
- Fresh tuna and pike from abroad should not be eaten more than once a week.











0 Comments